Translate This Page
ASL2 – An Application Management Framework, for the growing competitive demands in Information Systems support & Maintenance.
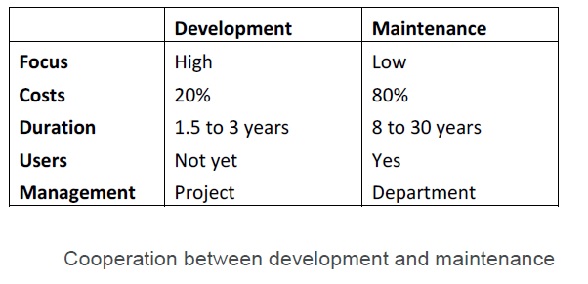
The industry in the past has emphasized mostly on system development, rather than on management, maintenance and enhancement of information systems and applications. The statistics below shows the danger of this practice, since most of the cost is incurred during the maintenance and enhancement stages of applications and information systems. In the resent past the trend in the industry shows many organizations are slowly shifting their emphasis more towards management, maintenance and enhancement of information systems and applications.
Application management is responsible with the support, maintenance and renewal of applications/information systems and data structures.
ASL – Application Service Library is the most significant application management process framework which provides with support for the implementation of application management in the organization. ASL is concerned with managing the support, maintenance, renewal and strategy of applications in an economically sound manner.
The ASL framework originates from an analysis of various knowledge domains related to ICT service, including ITIL and CMM. The framework comprises processes in the field of 'application management' and describes the definitions of these processes and the relationships between them. A detailed description of the processes forms part of the library, which consists of a framework, best practices, standard templates and a self-assessment.
The ASL framework can be used for all forms of application management, including for outsourced ICT services, internal ICT services as well as and all intermediate forms.
History of ASL
ASL (Application Services Library) was developed by a Dutch IT service provider called PinkRoccade in the 1990s and the framework and library was handed over to the ASL Foundation in 2001, which was made public in the same year. Since then the framework and the accompanying best practices have been maintained by the ASL BiSL Foundation. The current version is Version 2 (ASL2); published in the Netherlands in 2009. Within the foundation, number of large and small organizations of similar interests contributes to the development and building of the framework and the underlying best practices.
ASL®2 Framwork
ASL2 framework is formed by 4 layers: Process layer (26 processers), Cluster layer (6 clusters), Perspectives layer (2 perspectives) and Levels layer (3 levels)
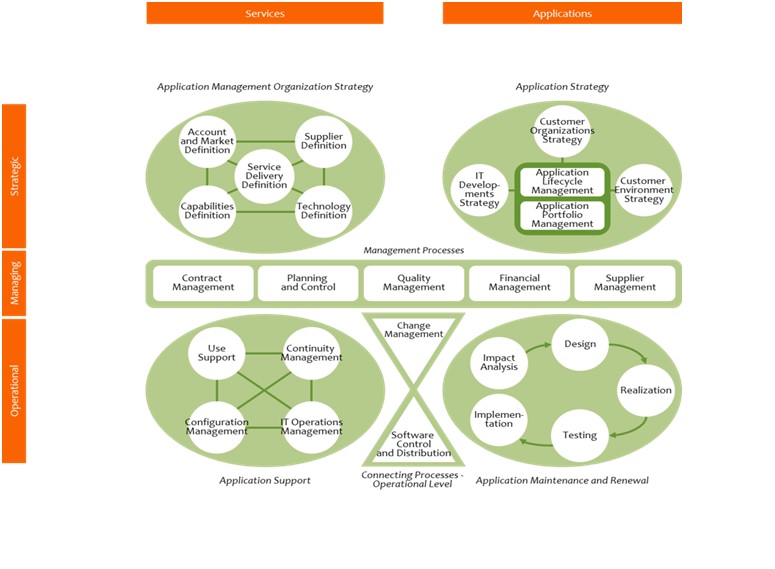
ASL2 Framework
ASL 2 Levels of Management
Application management comprises more than operational activities: ASL 2 also discerns between application management activities at the managing and strategic levels.
The tasks at the operational level deal with creating and changing the applications according to the users’ needs, and with supporting the day-to-day operation and use of the applications. Activities at the managing level control the operational service in order to comply with customer agreements and organizational preconditions regarding topics such as capacity, finance, agreements with suppliers and internal quality. The strategic level activities focus on the application(s) and the service organization that are needed for the next three to five years, and the development of scenarios to realize these changes.
ASL 2 Perspectives
ASL 2 has two perspectives:
- Service Orientation – providing services to external community.
- Application Orientation – knowing and anticipating developments in the business processes. (This requires knowledge of the business subject matter and is aimed at applications).
ASL 2 Clusters
ASL 2 comprises three levels and, in total, six process clusters. There are process clusters at the operational, managing and strategic levels. Each process cluster comprises a group of clearly interrelated processes with a collective goal. The six process clusters are:
- Application support;
- Application maintenance and renewal;
- Connecting processes;
- Management processes;
- Application strategy;
- Application management organization strategy.
Application Support cluster
The goal of the Application Support cluster is to ensure that the applications are optimally applied to support of the business processes, using the minimum resources and with the least possible operational disruptions.
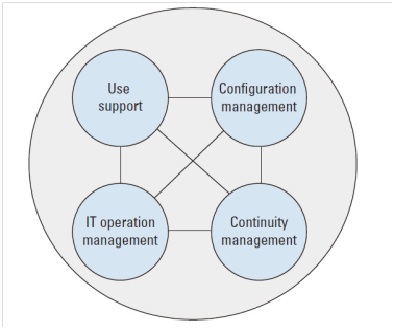
Process in Application Support cluster
Use Support process - ensures realization of optimal support in the use of applications by the best possible communication with customers and the best possible handling of calls about the use of – and possible deviations in – services, according to the agreements.
Configuration Management process - keeps a record of all application objects / configurations and services for which the application management organization has a responsibility, and provides accurate information about this to support other application management processes.
IT Operation Management process - ensures, monitors and guarantees that applications (or application components) display the correct and agreed behavior in operational situations, and that the services concerned also occur as agreed.
Continuity Management process - ensures continuity and the presence of adequate measures are available, which will, within a set time period and quality level, ensure adequate functioning even during extraordinary circumstances.
Connecting Processes cluster
The Connecting Processes - Operational Level cluster ensure the synchronization between the application support processes and the application maintenance and renewal processes. This cluster deploy changed software and data from application maintenance and renewal to application support.

Process in Connecting Processes cluster
Change Management process - ensures that a standardized working method is used for changing applications, so that harmonized and prioritized changes can be built to improve the supplied functionality of applications.
Software Control and Distribution process – ensures that the correct application objects (or information about them) available to the correct processes at the right time.
Application Maintenance and Renewal cluster
The goal of this cluster is to ensure that the applications are adapted to suit the changing demands and wishes resulting from changes in the environment and business processes.
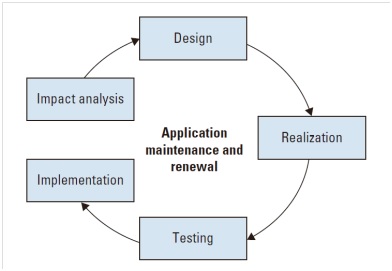
Process in Application Maintenance and Renewal cluster
Impact Analysis process - ensure that effective recording of sufficient reliable and accurate consequences of proposed changes in terms of effort, future events, use and operation, so that an ideal solution direction can be chosen.
Design process - set up and record the information system (user) specifications or changes in such a way that they can be easily realized and tested.
Realization process - converts the supplied designs or changes in designs, forming part of the design process, into concrete and correct changes to the automated information system.
Testing process - guarantee that the desired changes are realized according to specifications, and that applications show the correct behavior (after changes).
Implementation process - satisfy the necessary preconditions to enable error-free use of a new version of the application and completion of the maintenance process.
Management Processes cluster
The Management Processes cluster ensures that existing activities are performed according to goals, agreements and chosen strategies.
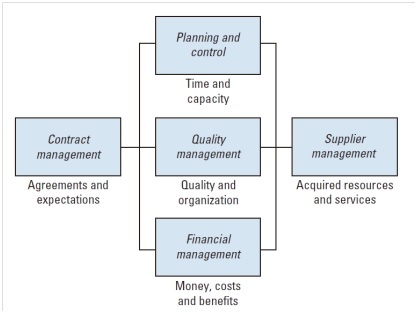
Process in Management Processes cluster
Contract Management process – ensures realization of services according to agreements (or deviating from these agreements by mutual consent) in order to fulfill or exceed customer expectations.
Planning and Control process - ensures that the agreed upon services are realized, using the agreed human resources capacity and in accordance with the agreed delivery date, by the correct deployment of human resources capacity at the right time.
Quality Management process - ensures the (internal and acquired) quality of the acquisition process, product, resources and organization by defining and monitoring these, and also ensuring that the relevant regulations are implemented and followed.
Financial Management process - ensures that the costs incurred for supplying / maintaining an application and/or services are planned and managed and are in balance with the benefits generated by application management.
Supplier Management process - responsible for agreements regarding services and/or solutions provided by third parties (suppliers), and for evaluating, monitoring and improving them.
Application Management Organization Strategy cluster
Application Management Organization Strategy cluster aims to ensure that the service organization’s policy and its future are correctly shaped.
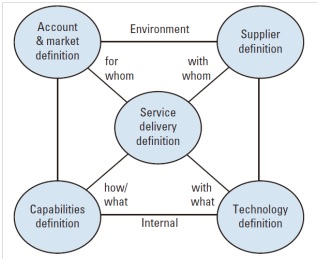
Process in Application Management Organization Strategy cluster
Account and Market Definition process - recognize the demands of future services for future customers and to make sure that the relationship and communication with the customers are good enough to realize this.
Capabilities Definition process - provide an overview of the demands to skills and expertise of the organization’s employees in the future.
Technology Definition process - select the tools [technology] that are used by the organization to realize the future services.
Supplier Definition process - pro-actively optimize the future service by determining the role of and the involvement of external suppliers, and translating this policy to a practical, functioning organization and structure.
Service Delivery Definition process - design the required services for a period of 2 or 3 years.
Application Strategy cluster
The goal of the Application Strategy cluster is development of a long-term strategy for the various application objects that form part of the information provisioning as a whole. This focuses on the future and the life cycle of the objects (applications) that are part of the information provisioning.
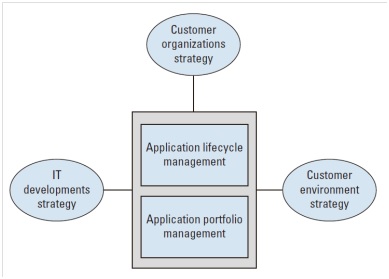
Process in Application Strategy cluster
IT Developments Strategy process – this determine the impact of technological developments on the application portfolio.
Customer Organizations Strategy process – determine the impact of developments in the user organization or the user organizations on the application portfolio.
Customer Environment Strategy process - determine the impact that developments in the environment of the customer organization or user organization have on the application portfolio.
Application Lifecycle Management process - determine the future strategy of an application, translated into actions, so that the application can provide support for the company processes in the future.
Application Portfolio Management process - align and coordinate the various components in an application landscape (or the entire information provisioning as a whole) and to mutually adjust and optimize the larger or radical investments and changes.
Application Management Standards and Maturity Models
ISO and NEN
In 2007 the NEN, the Dutch Standardization Institute, introduced the Dutch Standard for Application Management, the NEN 3434. This local standard was developed in cooperation with the ASL BiSL Foundation and was based on ASL.
In 2011, ISO/IEC came out with an initiative to develop international standard for application management, The ASL and the Dutch standard for application management, the NEN 3434, has been used to develop the international standard for Application Management. On August 1, 2015, the ISO/IEC 16350 for Application Management was published.
ISO 16350:2015 establishes a common framework for application management processes with well defined terminology that can be referenced by the software industry. It contains processes, activities, and tasks that apply during the stage of operation and use from the point of view of the supplier organization that enhances, maintains, and renews the application software and the software-related products such as data-structures, architecture, designs, and other documentation. It applies to the supply, maintenance, and renewal of applications, whether performed internally or externally with respect to the organization that uses the applications.
NEN 3434 standard enables the certification of application management process. This recognizes five maturity levels per process, where the certification has 4 levels (Levels 2, 3, 4 & 5)
Source: ASL BiSL Foundation